December 29, 2025 at 12:00 AM
In industrial operations, corrosion is one of the most significant threats to asset integrity, safety, and operational efficiency. Among the many factors that influence corrosion, the galvanic series plays a crucial role in understanding how different metals behave when connected in the same environment.

For industrial B2B companies dealing with piping, structural steel, equipment, and long-term storage, understanding the galvanic series is critical for corrosion prevention, preservation management, and asset protection.
What is the Galvanic Series?
The galvanic series is a list of metals and alloys ranked according to their electrochemical nobility in a specific environment, most commonly seawater or industrial electrolytes. It predicts which metals are more likely to corrode when two dissimilar metals are in electrical contact.
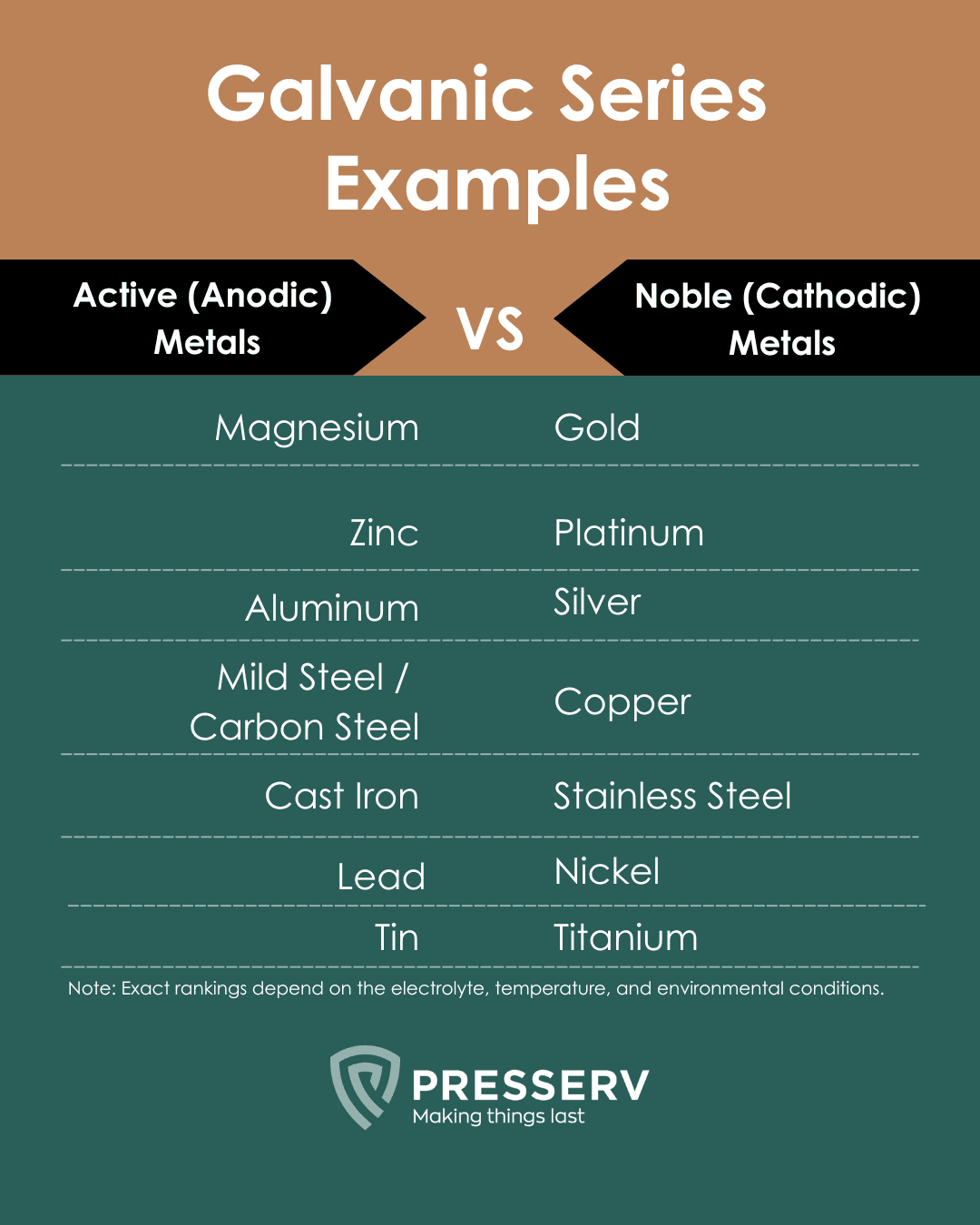
Anodic (active) metals
Found at the top of the series; these metals corrode more easily.
Cathodic (noble) metals
Found at the bottom; these metals resist corrosion and remain protected.
When two dissimilar metals are joined in an electrolyte, the less noble metal acts as the anode and corrodes, while the more noble metal acts as the cathode and is protected. This phenomenon is known as galvanic corrosion, a key consideration for industrial preservation.
Galvanic Series Examples
In seawater (a common reference electrolyte), the galvanic series ranks metals approximately as follows:
Key Takeaway
Metals further apart in the series will corrode more aggressively if connected. For example, connecting magnesium to copper in seawater without protection can cause rapid corrosion of magnesium.
The Importance of the Galvanic Series in Industrial Asset Management
For companies involved in rig stacking, preservation of rotating equipment, and long-term storage, understanding the galvanic series is essential for:
Material Selection
Choosing compatible metals minimizes galvanic corrosion in piping, heat exchangers, valves, and structural steel.
Corrosion Prevention
Protects critical assets during lay-up periods, cold or warm stacking, and idle equipment storage.
Preservation Planning
Guides the application of protective coatings, dehumidification solutions, VCI films, and other asset protection measures.
Cost Management
Reduces maintenance costs, unplanned downtime, and asset replacement due to corrosion failures.
Specifically, what does the galvanic series mean for corrosion prevention?
Understanding the galvanic series is not just theoretical—it informs real-world preservation strategies:
Equipment and Spare Part Preservation
Selecting compatible metals and applying physical or chemical preservation techniques—without using electrical or cathodic/anodic protection—prevents corrosion during the storage of pumps, heat exchangers, valves, and structural steel.
Rig Stacking and Asset Protection
During cold or warm stacking of offshore rigs, galvanic considerations dictate which materials require VCI films, protective coatings, or dehumidification solutions to prevent corrosion.
Pipeline Corrosion Management
In pipelines, galvanic series knowledge guides pipe material selection, cathodic protection, and inspection schedules for internal and external corrosion.
Marine and Humid Environments
Dehumidification solutions and asset protection films mitigate galvanic corrosion for equipment in atmospheric storage tanks, cooling towers, or idle machinery exposed to moisture.
Reducing Galvanic Corrosion
There are several strategies industrial operators can use to minimize galvanic corrosion risks:
Select metals close in the Galvanic Series: Reduces potential difference and corrosion rate.
Apply insulating materials: Use non-conductive gaskets, coatings, or spacers to prevent electrical contact.
Use protective coatings and films: VCI films, fire-retardant protective films, and anti-corrosion coatings shield anodic metals.
Implement cathodic protection: Sacrificial anodes or impressed current systems protect more noble metals in pipelines and tanks.
Environmental control: Reduce humidity and moisture exposure with dehumidification solutions, especially for long-term storage or cold stacking.
Conclusion
The galvanic series is a foundational concept for industrial corrosion management, informing material selection, preservation strategies, and asset protection planning. Understanding which metals are anodic or cathodic helps industrial operators prevent corrosion, maintain asset integrity, and optimize equipment lifespan.
For companies in offshore oil and gas, petrochemicals, mining, renewable energy, and other industrial sectors, integrating galvanic series knowledge with preservation management, rig stacking, and dehumidification solutions ensures long-term operational reliability.
Ready to learn more about reducing galvanic corrosion? Contact us to learn how our corrosion experts and preservation specialists can help your industrial assets withstand galvanic corrosion and remain operationally reliable.



